DAY 15: Khamis, 25 Jun 2015. 8th Ramadan
Greetings:
guten morgen - good morning
guten Tag - good day
gute nacht - good night
guten morgen - good morning
guten Tag - good day
gute nacht - good night
Ich = Saya
Sie = Awak (formal)
du = Kau (informal)
Sie = Awak (formal)
du = Kau (informal)
kebanyakan Kata kerja berakhir "en", contoh:
makan = Essen
minum = trinken
pergi = gehen
mahu = mochten
berlari = laufen
Extra note: This is infinitive verb: verb in it's raw, natural state. In German it usually end with 'en'. In English, infinitives start with to (to go, to eat, to drink, to laugh, etc].
kalau Ich, drop n [biasa berakhir dengan e]:
Ich gehe = Aku pergi
Ich trinke = Aku minum
Ich laufe = aku berlari
ich esse = Aku makan
Ich mochte ... = Aku mahu ...
Ich mochte Essen = Aku mahu makan
*bila ada dua kata kerja dalam satu ayat, hanya kata kerja pertama yang di-conjugate.
kalau du, drop en, tambah st [biasa berakhir dengan st atau βt]
Ayat tanya: du selepas kata kerja (conjugate) + another kata kerja (raw):
mochtest du ~ (mahukah Kau ~)
mochtest du Essen = mahukah kau makan?
mochtest du Laufen = mahukah kau berlari?
Ayat penyata: du di depan sebelum kata kerja:
du gehst = Kau pergi
du trinkst = Kau minum
Du isst = Kau makan (special case Essen jadi isst)
Sample of basic rules, depends on 'who' related in the sentence:
Machen = to make
Ich mache = I make
Du machst = you make
Er / es / sie macht = it make [er - masculine, es - neuter, sie - feminine noun]
wir machen = We make
Ihr macht = You (all) make
Sie / sie machen = She (formal) / They make
Extra notes: Different way of saying you:
du - talking to one friend, informal
Sie - talking to a person in formal way [capital S, lowercase sie = she]
Ihr - talking to group of people
Example:
Sie gehen zum verkaufstelle = Awak pergi ke kedai [no conjugation for Sie]
Du gehst zum verkaufstelle = Kau pergi ke kedai
Ich gehe zum verkaufstelle = Saya pergi ke kedai
have = haben
I have = Ich habe
You have = du hast (special case buang 'b')
Asas kata tanya:
wo = where
wer = who
was = what
wenn = when
wie viel = how much
--> Wie viel Uhr? = how much time? / what is the time?
Was mochtest du? = what you want?
Wie gehts dir? - How are you?
wie alt bist du? - How old are you
Wo wohnst du? - Di mana kau tinggal
*remember in question, 'du' is after the verb.
Sample:
Ich mochte gehen = I want to go
Wo gehst du? = Where you want to go?
Ich mochte zum bazaar Ramadhan gehen. = I want to go to Bazaar Ramadhan.
*If there are 2 verbs in one santence, the second verb will be push at the end of sentence.
zum = to (place)
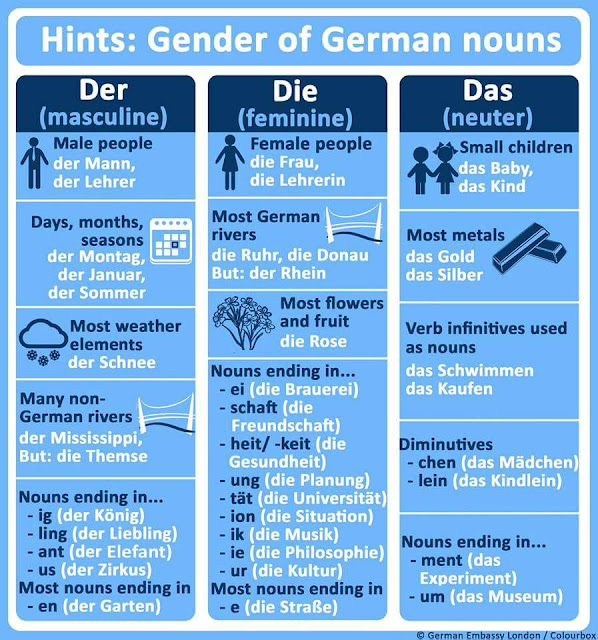
GENDER IN DEUTSCH:
Masculine: der
Femenine: die
Neuter: das
Femenine: die
Neuter: das
Cara tanya soalan: "hallo, ich habe eine Frage"
Habe = have
Eine = a
Frage = question
Habe = have
Eine = a
Frage = question
a:
Femenine: Die ➡ eine
Masculine: Der ➡ ein
Neuter: Das ➡ ein
Femenine: Die ➡ eine
Masculine: Der ➡ ein
Neuter: Das ➡ ein
Bis = until
Bist = are
Gehts = khabar
Gehst = pergi (untuk kau)
Bist = are
Gehts = khabar
Gehst = pergi (untuk kau)
Genau = exactly
richtig = betul
Sehr = sangat
alles = all
klar = fine
tut mir leid = I am sorry
langsam bitte = slowly please
---
Random word translated with google translate:
wie geht es Ihnen = how is it going?
was machst du von Beruf? = What is your job?
Vielen Dank = Many thanks.
Viel Spass beim lernen = have fun with your study
Guten Appetit = Enjoy your meal
*Note finally done on 26/12/2015, 7pm.
richtig = betul
Sehr = sangat
alles = all
klar = fine
tut mir leid = I am sorry
langsam bitte = slowly please
---
Random word translated with google translate:
wie geht es Ihnen = how is it going?
was machst du von Beruf? = What is your job?
Vielen Dank = Many thanks.
Viel Spass beim lernen = have fun with your study
Guten Appetit = Enjoy your meal
*Note finally done on 26/12/2015, 7pm.